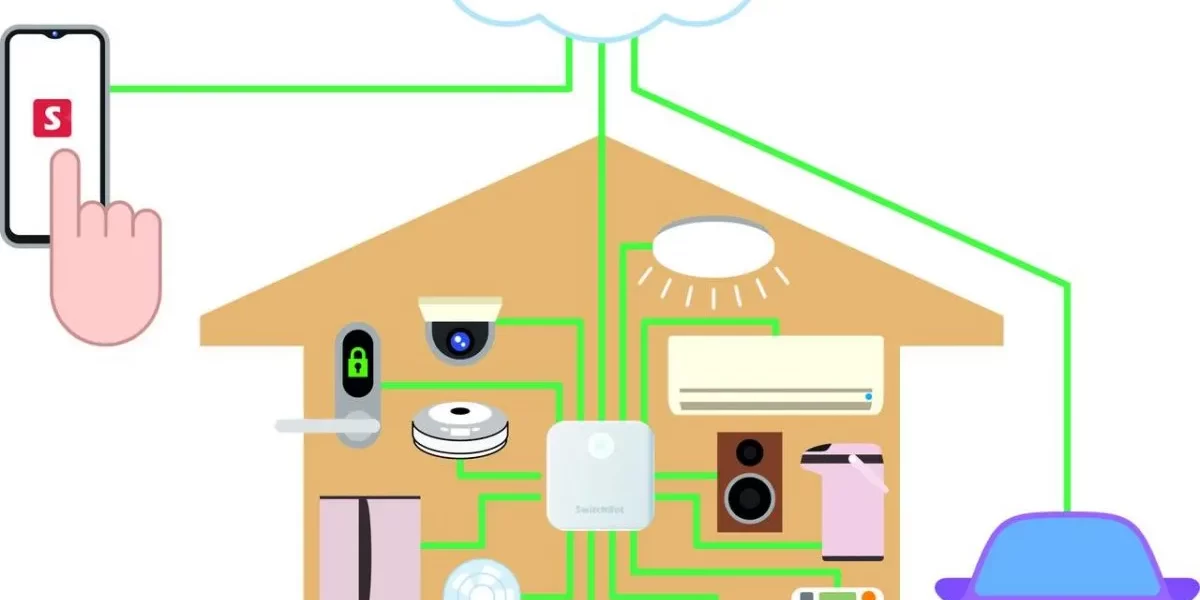
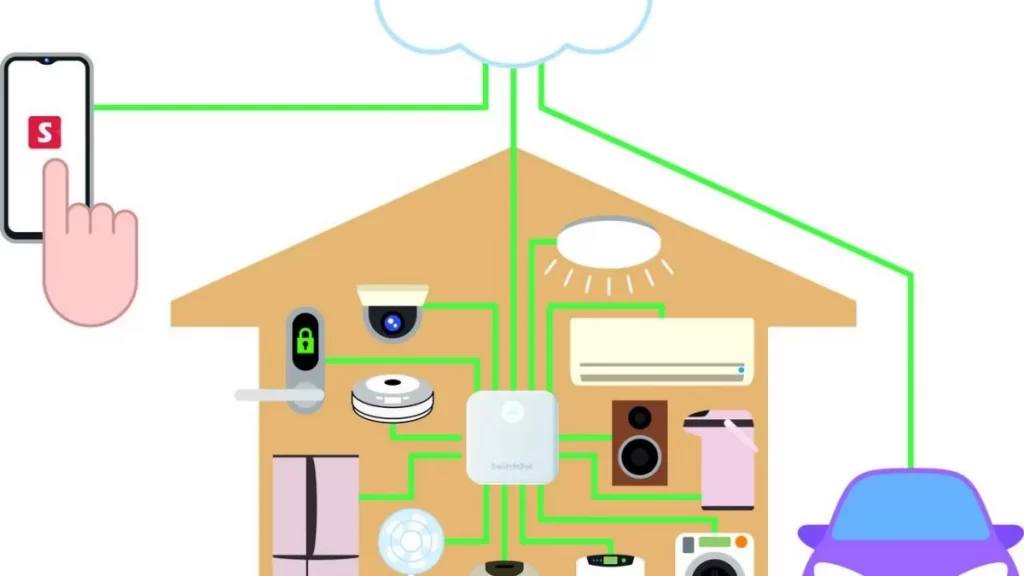
Understanding how smart home hubs work is essential for anyone looking to create a truly connected and automated living experience. Smart home hubs serve as the central nervous system of modern home automation, orchestrating communication between diverse IoT devices while providing seamless control through unified platforms.
What is a Smart Home Hub and Why Do You Need One?
A smart home hub functions as the central command center that connects and controls all your smart devices under one unified system. Think of how smart home hubs work as similar to a conductor leading an orchestra – each device plays its part while the hub ensures perfect harmony and timing throughout your connected home ecosystem.
Modern smart home hubs eliminate the frustration of managing multiple apps by creating a single point of control for everything from smart lighting and climate control to home security systems and entertainment devices. With the smart home market projected to reach $1.4 trillion by 2034, understanding hub functionality becomes crucial for maximizing your investment in home automation technology.
Core Components That Make Smart Home Hubs Work
Central Processing and Communication Protocols
Smart home hubs utilize multiple communication protocols simultaneously to ensure broad device compatibility. The most common protocols include:
Wi-Fi Connectivity: Provides high-bandwidth communication for data-intensive devices like smart cameras, streaming devices, and smart displays. Most hubs connect directly to your home network via ethernet or wireless connections.
Zigbee Protocol: Creates a mesh network that allows devices to communicate with each other while extending range throughout your home. This low-power protocol is ideal for smart switches, sensors, and smart locks that need to operate reliably without frequent battery changes.
Z-Wave Technology: Another mesh networking protocol that operates on a different frequency than Zigbee, providing excellent reliability for home automation devices. Z-Wave excels in scenarios requiring guaranteed message delivery, making it perfect for critical applications like smart security systems.
Matter Protocol: The newest universal standard that enables seamless interoperability between devices from different manufacturers. Matter represents the future of smart home connectivity by eliminating compatibility concerns between Google Assistant, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit ecosystems.
Local Processing vs Cloud Connectivity
Advanced smart home hubs process many commands locally, reducing latency and maintaining functionality even when internet connections are disrupted. This local processing capability ensures that essential functions like smart lighting, climate control, and security systems continue operating during network outages.
Cloud connectivity enhances hub functionality by enabling remote access, over-the-air updates, and integration with online services. When you’re traveling, cloud connectivity allows you to monitor home security cameras, adjust your smart thermostat, or control automated shades from anywhere in the world.
How Different Hub Types Serve Various Smart Home Needs
Standalone Dedicated Hubs
Traditional standalone hubs like Samsung SmartThings, Hubitat Elevation, and Aeotec Smart Home Hub focus exclusively on device coordination and automation. These hubs excel in complex automation scenarios where precise timing and reliable device communication are paramount.
Dedicated hubs typically offer the most robust automation capabilities, supporting complex conditional logic that can trigger multiple device actions based on sensor inputs, time schedules, or user presence. For example, a single automation routine could dim smart lighting, adjust climate control, arm your security system, and close motorized blinds when you leave for work.
Voice Assistant Integrated Hubs
Amazon Echo devices, Google Nest Hub displays, and Apple HomePod systems combine hub functionality with voice control capabilities. These integrated solutions simplify smart home control by allowing natural language commands while serving as the central coordination point for connected devices.
Voice-controlled hubs excel in households where convenience and ease of use take priority over advanced automation features. The integration of AI-powered automation enables these hubs to learn user preferences and suggest optimization routines that improve energy efficiency and enhance daily convenience.
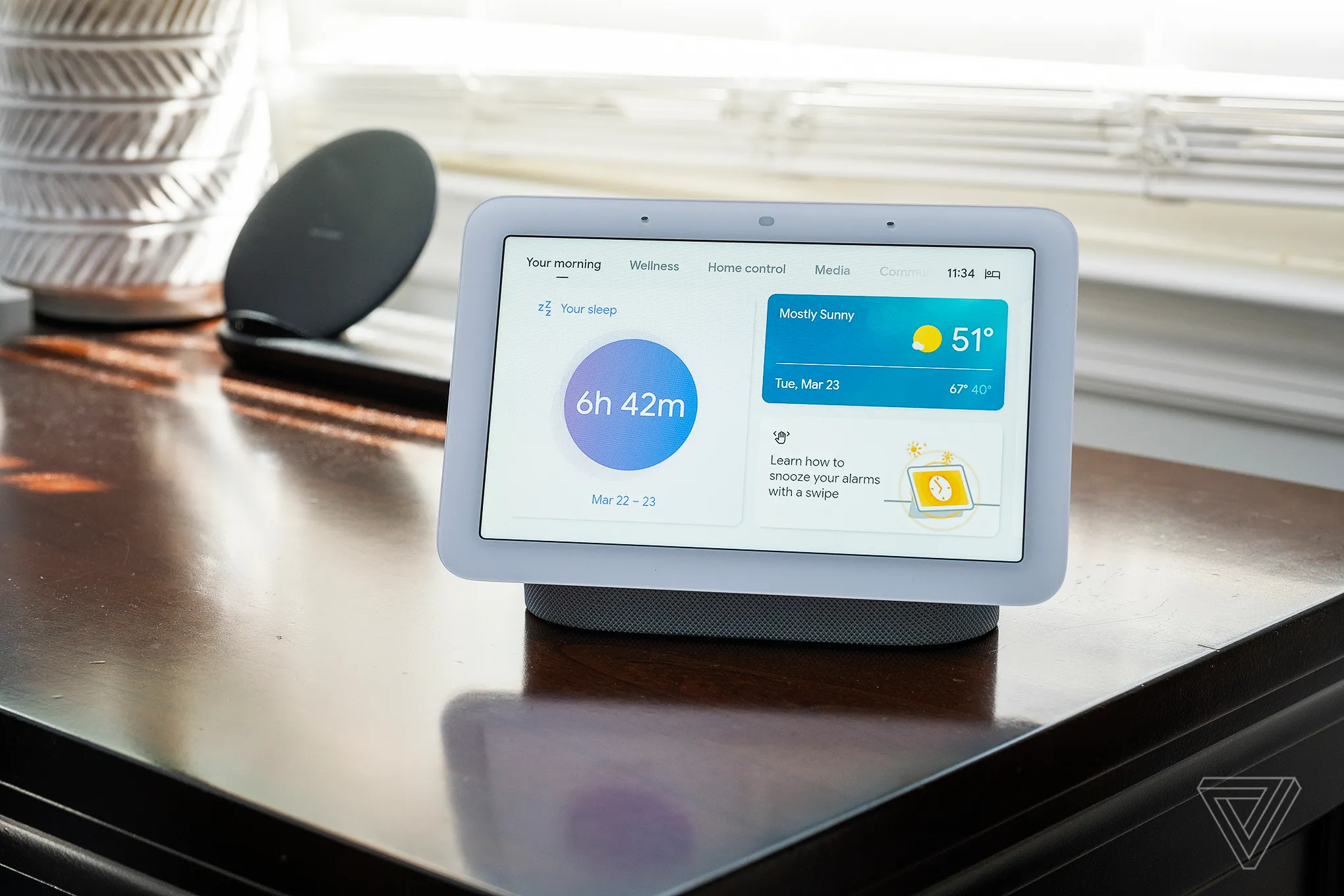
Multi-Function Smart Displays
Smart displays like Google Nest Hub Max and Amazon Echo Show provide visual interfaces alongside hub functionality. These devices offer touchscreen control, video streaming capabilities, and serve as digital photo frames when not actively managing your smart home ecosystem.
The visual interface proves invaluable for controlling smart cameras, viewing security system status, managing smart home apps, and displaying real-time information from IoT devices throughout your home. Many users find the combination of voice control and visual feedback creates the most intuitive smart home experience.
Setting Up Your Smart Home Hub for Optimal Performance
Network Infrastructure Requirements
Successful hub operation requires robust network infrastructure capable of handling multiple simultaneous device connections. A reliable mesh network system ensures consistent connectivity throughout your home, preventing device dropouts that can disrupt automation routines.
Position your hub centrally within your home to optimize wireless signal coverage. Avoid placing hubs near sources of electromagnetic interference like microwaves, baby monitors, or other wireless routers operating on similar frequencies.
Device Discovery and Pairing Process
Modern hubs streamline device addition through automated discovery processes. Most smart home devices announce their presence when powered on, allowing hubs to detect and suggest pairing automatically. This plug-and-play functionality has largely eliminated the complex setup procedures that once deterred smart home adoption.
The pairing process typically involves putting devices into pairing mode, selecting them from the hub’s interface, and following simple setup wizards. Advanced hubs can automatically download device drivers and configure optimal settings based on device type and installation location.
Creating Automation Routines and Scenes
Effective automation requires thoughtful scene creation that addresses real-world usage patterns. Start with simple routines like “Good Morning” scenes that gradually brighten smart lighting, adjust your smart thermostat to comfortable temperatures, and provide weather updates through connected smart speakers.
Advanced users can create complex conditional automations that respond to multiple triggers. For instance, combining motion sensors with smart cameras can create intelligent security routines that only activate recording and send alerts when unauthorized movement is detected, reducing false alarms while maintaining comprehensive home security.
Advanced Hub Features That Transform Smart Home Experience
AI-Powered Learning and Optimization
Leading smart home hubs incorporate machine learning algorithms that analyze usage patterns to suggest automation improvements. These systems learn your preferences for lighting levels, temperature settings, and device usage timing to create increasingly personalized automated experiences.
AI-driven optimization can significantly impact energy efficiency by automatically adjusting smart thermostats, managing smart lighting based on occupancy, and coordinating smart appliances to operate during off-peak energy periods. Some users report 15-25% reductions in utility costs through intelligent automation.
Advanced Security Integration
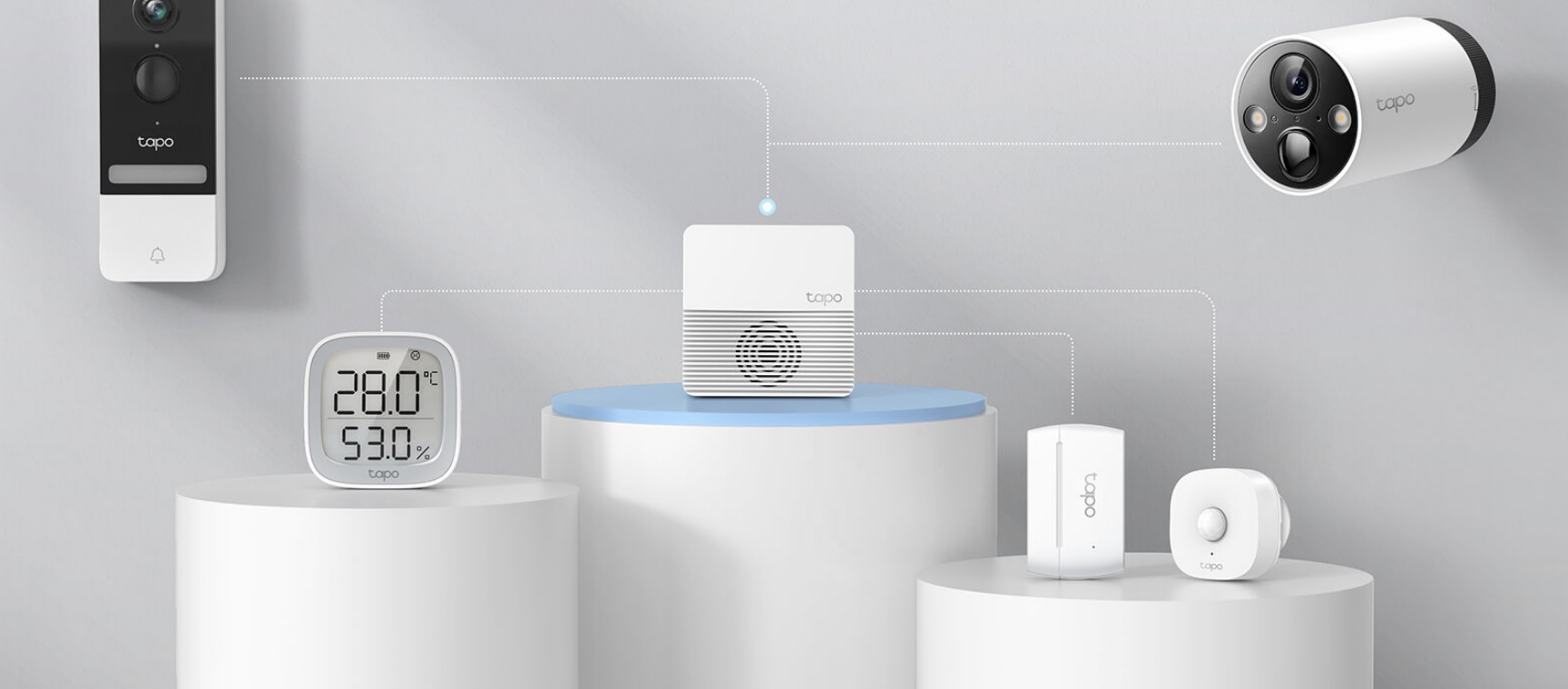
Modern hubs serve as comprehensive security command centers, coordinating smart locks, security cameras, motion sensors, and smart doorbells into cohesive protection systems. Integration capabilities allow hubs to automatically lock doors, activate recording, and send real-time alerts when security breaches are detected.
Biometric authentication features enable hubs to recognize individual family members and adjust automation routines accordingly. When the system recognizes your arrival, it can disarm security systems, adjust lighting preferences, and prepare your smart home environment to match your personal preferences.
Health and Wellness Monitoring
Advanced hubs integrate with health-focused IoT devices to monitor air quality, track sleep patterns, and optimize environmental conditions for wellness. Smart air purifiers, humidity sensors, and temperature monitors work together to maintain optimal indoor environmental quality automatically.
Some hubs can detect unusual activity patterns that might indicate health emergencies, particularly valuable for elderly residents. Integration with wearable devices enables hubs to adjust automation routines based on activity levels, stress indicators, and sleep quality metrics.
Troubleshooting Common Smart Home Hub Issues
Connectivity Problems and Solutions
Network connectivity issues represent the most frequent hub-related problems. When devices become unresponsive, systematic troubleshooting should begin with checking network connectivity, verifying device power status, and ensuring hub firmware remains current.
Interference from neighboring wireless networks can disrupt hub communication, particularly in dense residential areas. Switching to less congested wireless channels or upgrading to newer protocol versions often resolves persistent connectivity issues.
Device Compatibility Challenges
Despite improving standardization efforts, device compatibility remains a consideration when expanding smart home systems. Before purchasing new devices, verify compatibility with your existing hub and check for any required firmware updates or additional configuration steps.
The introduction of Matter protocol promises to eliminate most compatibility concerns, but implementation remains inconsistent across manufacturers. When possible, choose devices that explicitly support your hub platform to ensure seamless integration and full feature availability.
Performance Optimization Strategies
Hub performance can degrade over time as device counts increase and automation complexity grows. Regular maintenance including firmware updates, automation routine reviews, and periodic system reboots helps maintain optimal performance.
Consider hub placement optimization if you experience inconsistent device responsiveness. Moving hubs to more central locations or adding mesh network extenders can significantly improve communication reliability throughout larger homes.
Future Trends Shaping Smart Home Hub Evolution
Enhanced AI Integration and Natural Language Processing
The next generation of smart home hubs will feature dramatically improved natural language processing capabilities, enabling more conversational interactions and complex command interpretation. Users will be able to describe desired outcomes in natural language rather than learning specific command syntax.
Advanced AI integration will enable hubs to proactively suggest automation improvements, predict maintenance needs for connected devices, and automatically optimize energy usage patterns based on utility rates and usage history.
Increased Focus on Privacy and Local Processing
Growing privacy concerns are driving development toward increased local processing capabilities. Future hubs will perform more functions without requiring cloud connectivity, giving users greater control over their personal data while maintaining advanced functionality.
Enhanced encryption and user authentication features will become standard, protecting smart home networks from cybersecurity threats while maintaining the convenience that makes smart home technology appealing.
Integration with Urban Infrastructure
Smart home hubs are evolving to integrate with broader smart city initiatives, enabling coordination between home automation systems and municipal services. This integration could optimize energy usage based on grid demand, coordinate with public transportation schedules, and enhance emergency response capabilities.
The convergence of home automation with urban infrastructure represents a significant opportunity to improve energy efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and enhance quality of life through intelligent coordination between individual homes and community resources.
Maximizing Your Smart Home Investment Through Strategic Hub Selection
Choosing the right smart home hub requires careful consideration of your current needs, future expansion plans, and technical comfort level. Start with a clear assessment of which devices you want to control and the automation complexity you desire.
Consider long-term compatibility when making hub investments. Platforms with strong developer ecosystems and regular updates are more likely to remain relevant as smart home technology continues evolving. The rapid pace of innovation means today’s cutting-edge features may become tomorrow’s standard functionality.
Budget considerations should account for both initial hub costs and ongoing expansion expenses. While premium hubs offer advanced features, many users find mid-range options provide excellent value when starting their smart home journey.
Understanding how smart home hubs work empowers you to make informed decisions about home automation investments while avoiding common pitfalls that can lead to frustration and wasted resources. Whether you choose a simple voice-controlled hub or an advanced automation platform, the key lies in selecting technology that matches your lifestyle and grows with your evolving needs.
The smart home revolution is just beginning, and hubs represent the foundation upon which increasingly sophisticated automation systems will be built. By investing in quality hub technology today, you’re positioning yourself to take advantage of emerging innovations that will continue transforming how we interact with our living spaces for years to come.